Research
Jump to Research Topics, Project
Research Topics
AI Assistance for Interpretation and Diagnosis
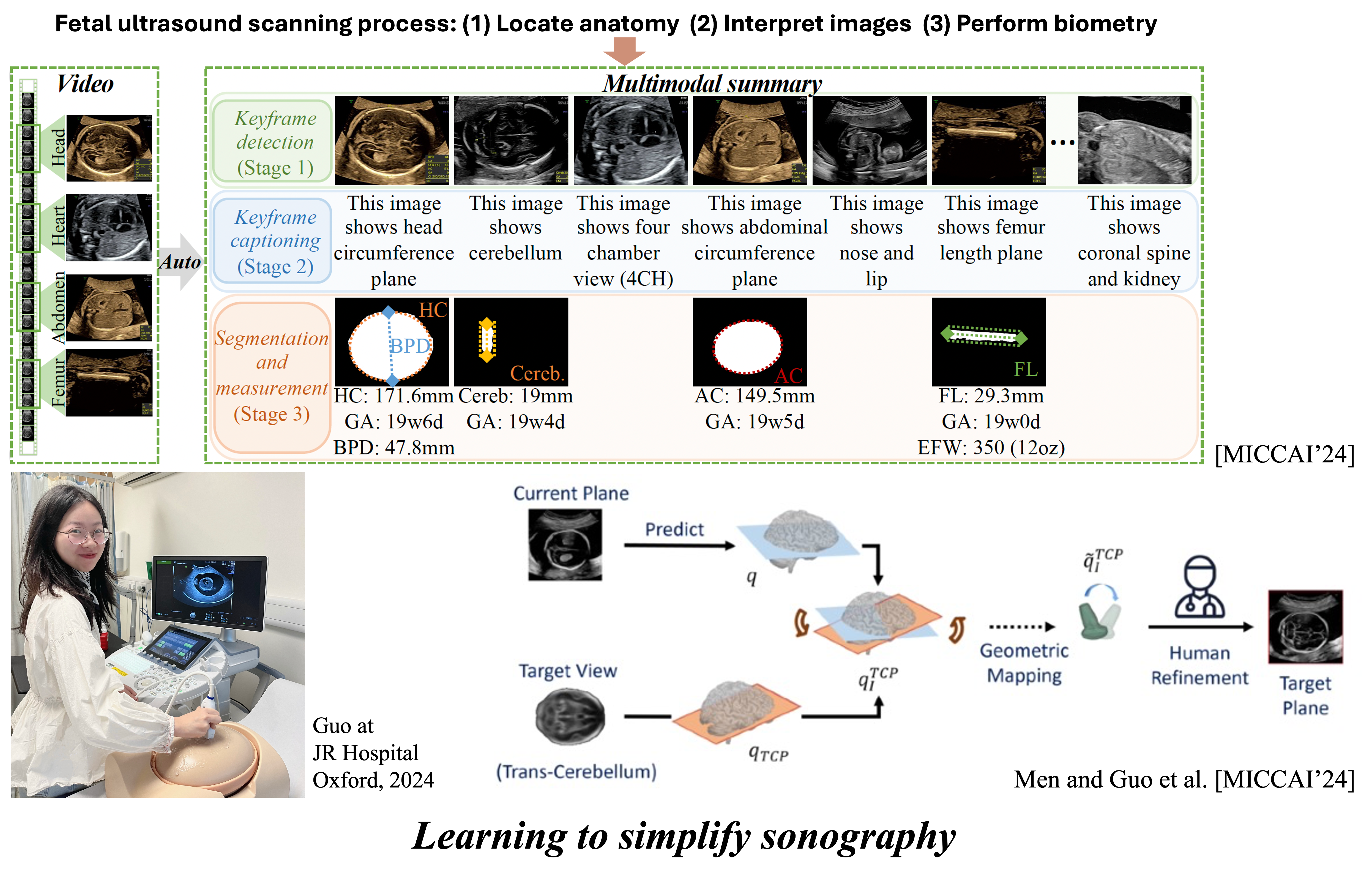
Ultrasound examinations generate complex, unstructured data in the form of video, making interpretation both time-intensive and skill-dependent. Our research focuses on post-scan AI systems that can analyze, summarize, and extract key diagnostic information from full-length ultrasound videos. These methods can help standardize interpretations and accelerate workflows for both experienced sonographers and trainee sonographers.
Relevant Publications:
- MMSummary: Multimodal Summary Generation for Fetal Ultrasound Video [MICCAI’24]
- U2-BENCH: Benchmarking Large Vision-Language Models on Ultrasound Understanding [ICLR’26]
Sonography with Language Guidance
Freehand ultrasound examinations require significant clinical skill and are time-consuming. To support both learning and execution, we develop interactive AI systems that use natural language to provide real-time feedback and guidance during the scanning process. By integrating vision-language models trained on ultrasound data, we can respond to user queries, identify anatomical landmarks, and give step-by-step instructions. This approach empowers novice users to perform scans more confidently and allows experts to benefit from intelligent assistance in complex scenarios.
Relevant Publications:
- A visually grounded language model for fetal ultrasound understanding [Nature Biomedical Engineering’26]
- U2-BENCH: Benchmarking Large Vision-Language Models on Ultrasound Understanding [ICLR’26]
Sonography with Spatial Guidance
Accurate ultrasound imaging depends heavily on the operator’s ability to correctly position and manipulate the probe. This research focuses on incorporating spatial intelligence into AI systems that can guide or automate probe movements during scanning. By modeling expert scanning behaviors using pose estimation and motion feedback, we aim to develop systems that assist users in acquiring standard views and maintaining spatial consistency. These tools reduce inter-operator variability and enable more efficient, reproducible scans, especially in high-demand or low-resource clinical settings.
Relevant Publications:
- Pose-GuideNet: Automatic Scanning Guidance for Fetal Head Ultrasound from Pose Estimation [MICCAI’24]
Project
Automatic Ultrasound Video Summarization for Improved Diagnosis with Simplified Scanning Protocols
RGC Early Career Scheme (PI)